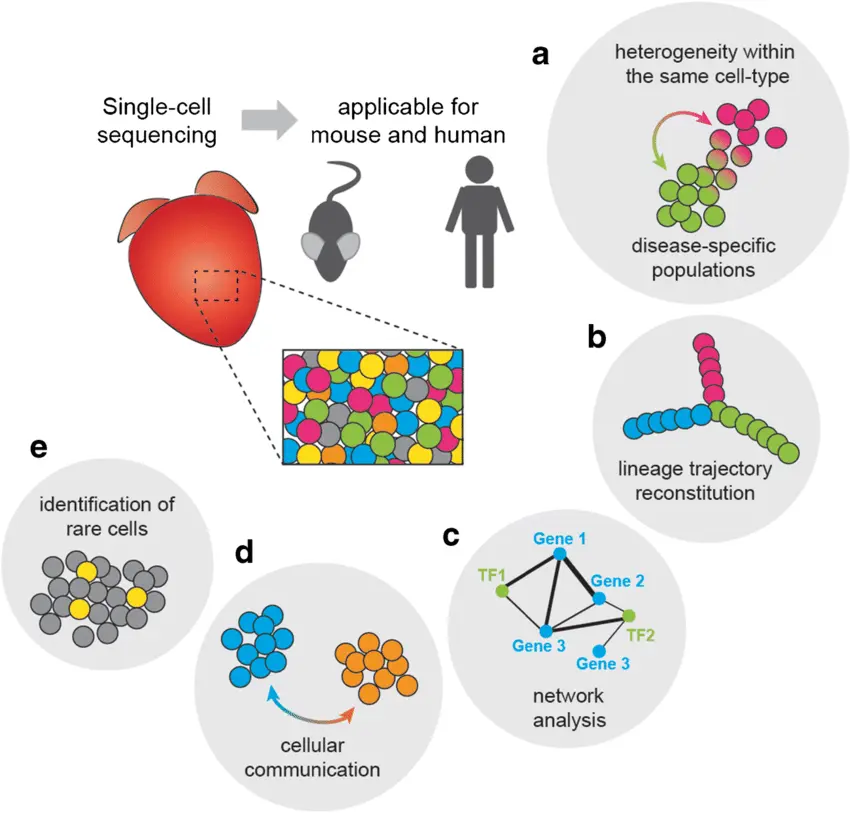
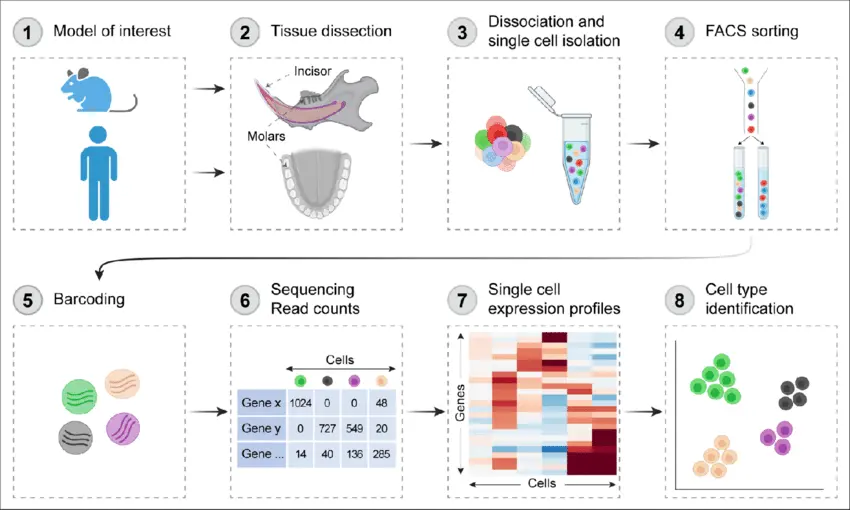
Applications
Single-cell sequencing analyzes nucleic acid sequences from individual cells using next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies. It provides detailed information on cellular variability and function within their microenvironment
What is Single-Cell Analytics?
Single-cell analytics is a transformative approach to studying biological systems at the most granular level. By analyzing individual cells, scientists can:
Understand Cellular Heterogeneity: Discover how cells with identical DNA function differently.
Track Cellular Dynamics: Investigate cellular responses to environmental changes, disease, or therapies.
Unlock Precision Medicine: Tailor treatments based on cellular-level data for better patient outcomes.